
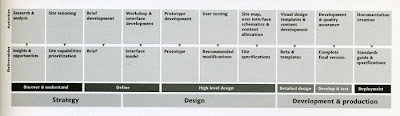
- define the problem
- develop a better understanding of the problem
- conceptualise the problem
- detail a design solution
- test or implement
The creative process
Creativity is:
- an approach
- skill
- characteristic
- talent
- any situation, problem or opportunity
- in business and life
The five step creative process:
- Preparation: immersion in a set of problematic issues that are interesting and arouse curiosity
- Incubation: ideas are churned around, below the level of consciousness, and unusual connections are made
- Insight: pieces of puzzle begin to fall into place
- Evaluation: deciding which insight is most valuable and worth pushing
- Elaboration: turning the insight into something real
Iterative processes

Design processes are difficult to standarise because:
- of their iterative, non-linear nature
- the needs of clients and users are different
- real life, with its changing market conditions and customer preferences, is much more dynamic, chaotic and fuzzy than a standard model can accomodate
- reach eventually a cut-off point
- commit to an agreed direction
- reduce the level of exploration and development of new ideas
- set the deadline is matter of experience and judgment
- have a defined set of project steps
- a timeframe
- a known, or at least expected, outcome, one that complies with an agreed checklist of performance criteria
- quality
- safety
- efficiency
- find ways to optimise production processes
- in communicating performance results against time and cost issues
- improve organisations performance and efficiency
- uninspiring 'assembly-line' solutions
- little dialogue or dabate between teams
- uninteresting results
Are more detailed and so are better suited to specific/individual needs.
They usually combine standard aspects with customised ones.
Design processes as a service offer
Within an organisation, certain processes may be unique to it for strategic reasons, and therefore need to remain confidential.
Other s can be sold as a consultancy offer.
_________________________________________
For Major project
As our project is 'discovery' itself, the Creative process suits it the best.
Preparation
Using the Storytelling technique we have listed a set of problematic and interesting issues on London tube platforms which we could find out or think of. It also shown possible solutions.
Incubation
Using brainstorm we have put down any possible, relevant or irrelevant ideas. We were looking into connecting the ideas in new, innovative or interesting way.
Insight
The analysis of the brainstorm was made and selected the most interesting and relevant solutions.
Evaluation
The best solution was chosen.
Elaboration
The process of final prototype has begone.
No comments:
Post a Comment